chemicals
PFAS Alternatives Exist

Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a large, diverse group of man-made chemical compounds with special water repellent and non-stick properties. Since the 1950s they have been used in a variety of applications including: cookware, food packaging, cosmetics, carpets, fire-fighting products, stain repellents, polishes, paints and coatings. Structurally, PFAS are organofluorine compounds, where multiple fluorine atoms are attached to a carbon atom. A PFAS can be any compound with a perfluorinated methyl group (–CF3) or a perfluorinated methylene group (–CF2–). PFAS compounds can be categorised in various ways and different chemical databases estimate there are between 4700 and 14700 PFAS compounds.
Strong, stable and persistent
The chain of carbon and fluorine atoms confers advantages and disadvantages to PFAS compounds. They are excellent surfactants and form strong interfaces between air and water. They are strongly water repellent and good at breaking up fatty materials, which is why they have been so widely used in consumer goods. However, the carbon-fluorine bond is incredibly stable, even under harsh conditions. PFAS are very resistant to degradation, they can persist for decades. Consequently, they are often called ‘forever compounds’.
We are all exposed to harmful PFAS compounds
Once released into the environment water-soluble PFAS spread rapidly. They move through soils, contaminate rivers, lakes, seas, drinking water sources and accumulate in fish and wildlife. We can be exposed to PFAS compounds through the food we eat and the water we drink. Additionally, since PFAS are often used in consumer products, they are found frequently in our homes. One studies estimated that 99% of Americans have at least two harmful forms of PFAS in their blood, and the situation is probably similar around the world. In humans even low concentrations of PFAS have been linked to a wide range of health problems. The effects include increased risk of certain types of cancer, reduced ability to fight infections, altered metabolism, decreased fertility, decreased fetal development and increased risk of obesity.
Bans and restrictions on PFAS will increase
In Europe the European Commission (EC) is introducing laws to ban all PFAS. If the legislation progresses as planned these compounds could be banned from around 2026. In 2016 the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) banned three PFAS chemicals from food packaging. Since 2023 California and New York have banned PFAS in paper-based food packaging and other states and taking similar action. It is widely assumed that the use of PFAS will be banned or severely restricted in the future. As a result, many industries are looking for substitutes or totally new alternatives.
The good news
Viable PFAS-free alternatives exist, and our clients are starting to adopt them.
NineSigma has identified alternatives to PFAS compounds for a diverse range of applications such as automotive, building and construction, textile, energy, household, marine, electronics, optical and consumer goods.
Here are 2 examples of NineSigma´s projects:
Case Study 1: Oil and Grease Resistant Coatings for Food Packaging
Our client manufactures high oil and grease resistant paper and board packaging for food. They were seeking sustainable (compostable, recyclable or biodegradable), no fluor-based, FDA/GRAS compliant coatings with very high oil and grease resistance (OGR). OGR is often measured using the ‘kit test’ (TAPPI Test Method T559) that rates OGR from 1 to 12. Our client was seeking the highest level of ORG, preferably a kit score of 12. Through our NineSigma networks and research expertise, we identified over 60 food-safe PFAS-free OGR coatings. Most of these had moderate OGR (kit 5 to 7) yet more than 25 coatings had very high OGR resistance (kit 9 to 12). They came from a wide range of approaches (for example: Lignin, CNC, HMRC, Chitosan, Water-based coatings) giving our client a good choice of alternative options. Our client selected 16 companies for non-confidential discussions, then prioritised the coatings that could be supplied in sufficient volumes for mass-market commercial applications and had good safety profiles when heated so the consumer could heat the food inside or on the coated board. To test and evaluate the most promising opportunities our client set up NDAs and MTAs with 9 companies. Testing is progressing well, and our client has options for new, food-safe, PFAS-free OGR coatings for a range of commercial applications.
Case Study 2: Low friction coatings for consumer goods
Our client who is a manufacturer of consumers goods were using PFAS containing low friction coatings for multiple products in their portfolio. They approached us with the aim of understanding the PFAS replacement strategies in low friction coating from different industries. They were seeking partners who already developed or willing to develop coating formulations that could be applicable to multiple surfaces, provide low coefficient of friction while mechanically and environmentally stable during use. NineSigma research team identified more than 150 organizations who are offering PFAS free low friction coatings by utilizing our broad open innovation network and publicly accessible scientific and business databases. Together with our client´s technical team, we evaluated these technologies based on their scientific merit and specifications and shortlisted them down to 50 technologies for in-depth evaluation. NineSigma team approached shortlisted companies for additional technical information and assessed technical specifications to identify the best-fit for client application.
At the end of the project NineSigma provided our client with detailed technical information for 20 approaches that could replace PFAS in low friction coatings for consumer products.
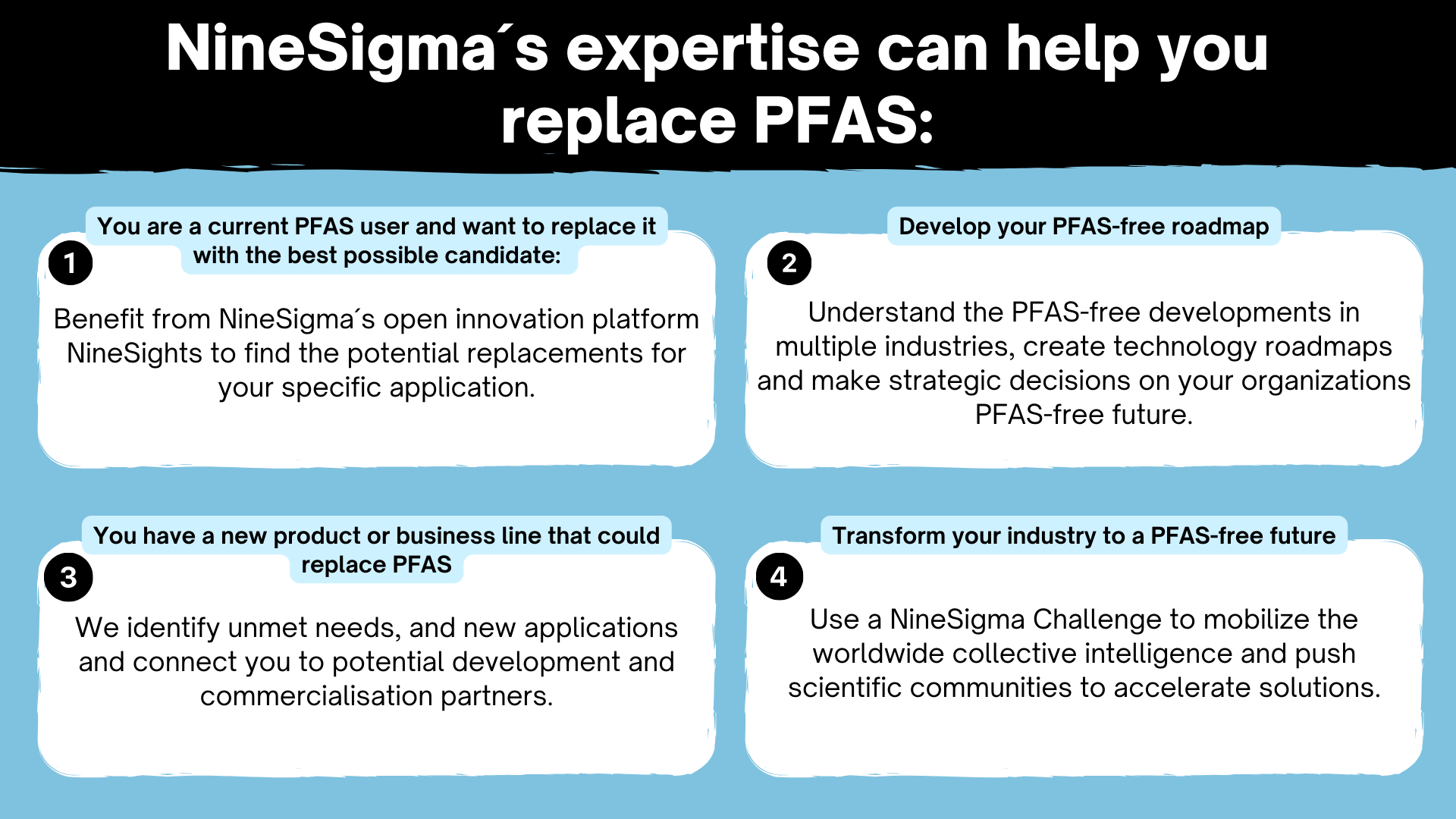
NineSigma´s expertise can help you replace PFAS:
Contact us if you are interested in finding PFAS alternatives for your products, applications or industry europe@ninesigma.com
Other topics :
Get in touch
NineSigma Europe BV
Koning Leopold I straat 3B-3000 LeuvenBelgium

+32 16 24 42 80

europe@ninesigma.com
USE CASES